China has added more than 34 gigawatts (GW) of nuclear power capacity over the last decade, bringing the country’s number of operating nuclear reactors to 55, the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) said.
This brings Beijing’s total net nuclear capacity to 53.2 GW as of April 2024, with an additional 23 reactors currently under construction.
In contrast, although the United States boasts the largest nuclear fleet globally with 94 reactors, it took nearly four decades for the US to achieve the same level of nuclear power capacity growth that China added in just ten years, as per the EIA’s analysis.
In 2014, China’s installed nuclear capacity was 19 GW, which surged to 53.2 GW by April 2024, marking an impressive 180 per cent increase.
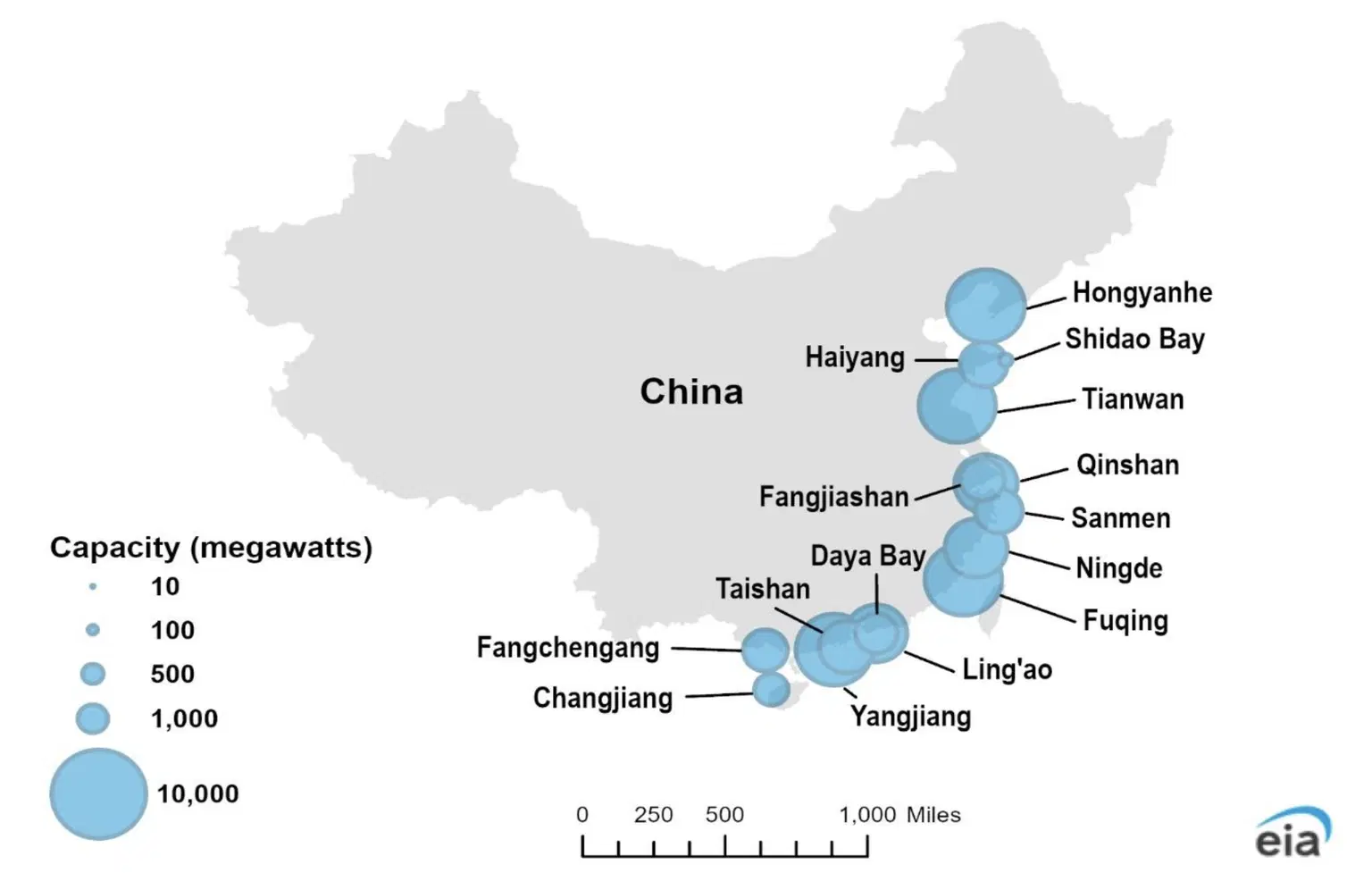
China’s nuclear fleet is concentrated near population centres in the eastern part of the country along the coast of the Pacific Ocean. Nuclear reactors are located from the Liaoning province in the north to the Hainan province in the south.
The country’s nuclear fleet consists mostly of pressurized water reactors (PWR), including the US Westinghouse-designed AP1000s, each with a capacity of 1,157 megawatts (MW), and the French Orano European Power Reactors, each with a capacity of 1,660 MW.
The US EIA has projected that the 23 reactors currently under construction in China will add about 23.7 GW to China’s existing nuclear power capacity over the next decade. The reactor unit designs are mostly PWR.
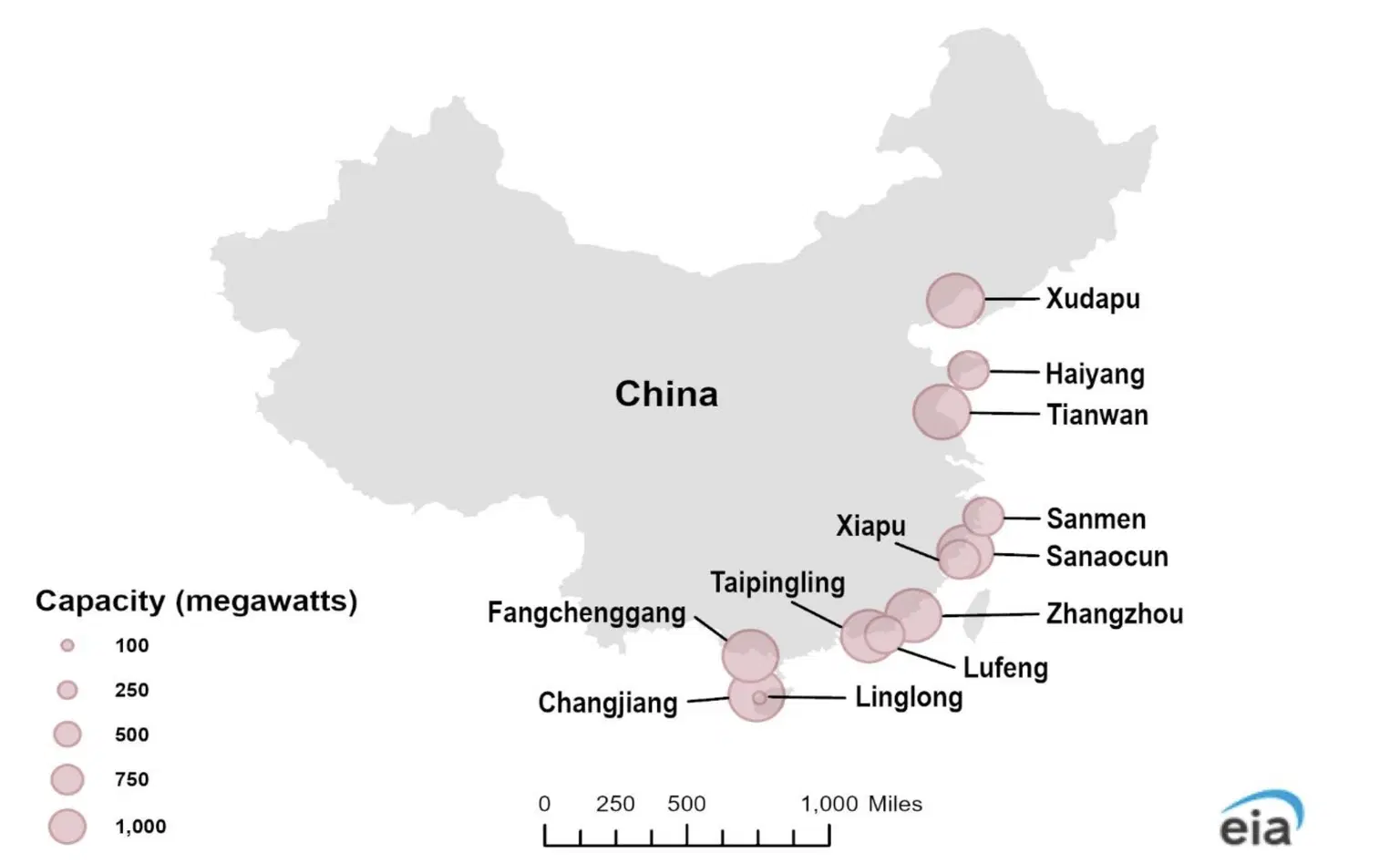
China is also building a Linglong-1 reactor, a small modular reactor in Changjiang of South China’s Hainan province.
The Linglong One, also known as the ACP100, is a multi-purpose pressurized water reactor (PWR) demonstration project invested in and controlled by China National Nuclear Power Co., Ltd. (CNNP), a subsidiary of China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC).
It is the world’s first third-generation SMR to pass a safety review by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
China has a goal to produce 10 per cent of electricity from nuclear by 2035 and 18 per cent by 2060, but as of April this year had not met its 2020 target to install 58 GW of nuclear capacity.
China has also not signed a pledge by 20 countries at the COP28 climate conference taking place in Dubai to triple nuclear power capacity by 2050.


